Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview of NRN Rights in Nepal
- Laws Governing NRNs in Nepal
- Constitution of Nepal
- National Civil Code, 2017
- Non-Resident Nepali Act, 2008
- Non-Resident Nepali Regulations, 2009
- Nepal Citizenship Act, 2006
- Immigration Act, 1992
- Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019 (FITTA)
- Who Are Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs)?
- Foreign Citizens of Nepali Origin
- Nepali Citizens Residing Abroad
- NRN Identification Card Process
- Application Steps
- Required Documents
- Visa Types for NRNs
- Tourist Visa
- NRN Visa
- Required Documents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Can NRNs Marry in Nepal?
- NRN Banking Rights
- Can NRNs Reacquire Nepali Citizenship?
- Property Acquisition Rights for NRNs
- Foreign Investment Rights for NRNs
- Conditions for NRN Investment
- Validity and Fees of NRN ID Card
- How to Get an NRN Card?
- Benefits of an NRN Card
- Can NRNs Keep Nepali Citizenship?
- Can NRNs Buy Land in Nepal?
Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs) play an essential role in Nepal’s economy and development. This guide explains the rights and legal provisions concerning NRNs under Nepali NRN law 2081.
-
Laws Governing NRNs in Nepal
NRN rights are regulated by various laws, including:
– The Constitution of Nepal
– National Civil Code, 2017
– Non-Resident Nepali Act, 2008
– Non-Resident Nepali Regulations, 2009
– Nepal Citizenship Act, 2006
– Immigration Act, 1992
– Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act, 2019 (FITTA)
These laws ensure that NRNs can maintain ties with their homeland and contribute to Nepal’s development.
-
Who are Non-Resident Nepalis (NRNs)?
NRNs are categorized into two groups:
– Foreign citizens of Nepali origin: These are individuals who were once Nepali citizens or whose parents or grandparents were Nepali citizens. They have acquired foreign citizenship from a country that is not a member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC).
– Nepali citizens residing abroad: Nepali citizens living in a foreign country for at least two years, engaging in business, employment, or studies. However, this excludes Nepalis living in SAARC countries or those working in foreign diplomatic missions.
-
NRN Identification Card Process
To be officially recognized as an NRN, individuals need to follow this process:
– Step 1: Submit an application to the relevant authority, such as the Nepali embassy or consulate, or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs in Nepal.
– Step 2: Pay the prescribed fees.
– Step 3: Receive the NRN Identity Card.
-
NRN Visa Types
NRNs can get two types of visas in Nepal:
– Tourist Visa: Issued upon arrival for short stays.
– NRN Visa: Issued for a maximum of 10 years, allowing extended stays in Nepal.
Documents required include:
– Online visa application form
– NRN ID card (original and photocopy)
– Valid passport
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can NRNs Marry in Nepal?
Yes, NRNs can marry in Nepal under the National Civil Code.
2. NRN Banking Rights in Nepal
NRNs with an NRN ID Card can open and operate bank accounts in Nepal for convertible currencies. This allows NRNs to easily manage their earnings and investments.
3. Can NRNs Reacquire Nepali Citizenship?
Yes, NRNs can reacquire Nepali citizenship by relinquishing their foreign citizenship. Applications can be submitted to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs or the local District Administration Office.
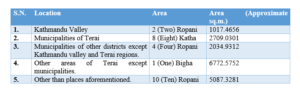
4. Property Acquisition Rights for NRNs
NRNs of Nepali origin can purchase property in Nepal, subject to the following conditions:
– They can buy land for personal or family use, within land ceiling limits.
– NRNs can also inherit ancestral property without government approval, provided they hold an NRN ID Card.
5. Foreign Investment Rights for NRNs
NRNs are classified as foreign investors under FITTA, allowing them to:
– Invest in shares and stocks
– Engage in venture capital and technology transfer
– Invest in Nepali companies and industries
6. Conditions for NRN Investment in Nepal
NRNs need to invest at least NPR 50 million in equity shares of a company, and the business must not fall under the negative list of FITTA. The sector must also qualify as an industry under the Industrial Enterprises Act, 2020.
7. NRN ID Card Validity and Fees
The NRN ID card is valid for:
– Up to 10 years for foreign citizens of Nepali origin.
– Up to 2 years for Nepali citizens residing abroad.
8. How can I get an NRN Card in Nepal?
For getting Non-Resident Nepali Card, the following steps must be taken:
- Visiting the Nepalese Consulate of Respective Country
- Requesting for Necessary Documents while filing for necessary details along with Photo
- Submission of Required Fees
- Issuance of NRN Identity Card
9. What are the benefits of an NRN Card?
Non-Resident Nepali’s are entitled to the following benefits:
- Right to Investment
- Repatriation of Money
- Purchasing of Land
10. Can NRNs keep Nepali citizenship?
In accordance with the recent amendment in the Citizenship Regulations, NRN are entitled to a Nepalese Citizenship. If NRN get citizenship of another Country, their Original Citizenship cannot be kept (i.e. ipso facto void).
11. Can NRNs buy land in Nepal?
NRN can definitely purchase land in Nepal for which they must apply to the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and submit all the required documents.




Pingback: E-Passport Making for Nepali (2024) - veshraj.com E-Passport Registration Nepal